Generators are one of the most powerful tools available to homeowners and businesses alike. Whether you’re looking to power your home in an emergency, or you’re just looking for a reliable source of energy, generators can provide the solution. In this article, we’ll take a look at how to harness the power of generators, and provide you with the information you need to make an informed decision about which type of generator is best for your needs.
Types of Generators
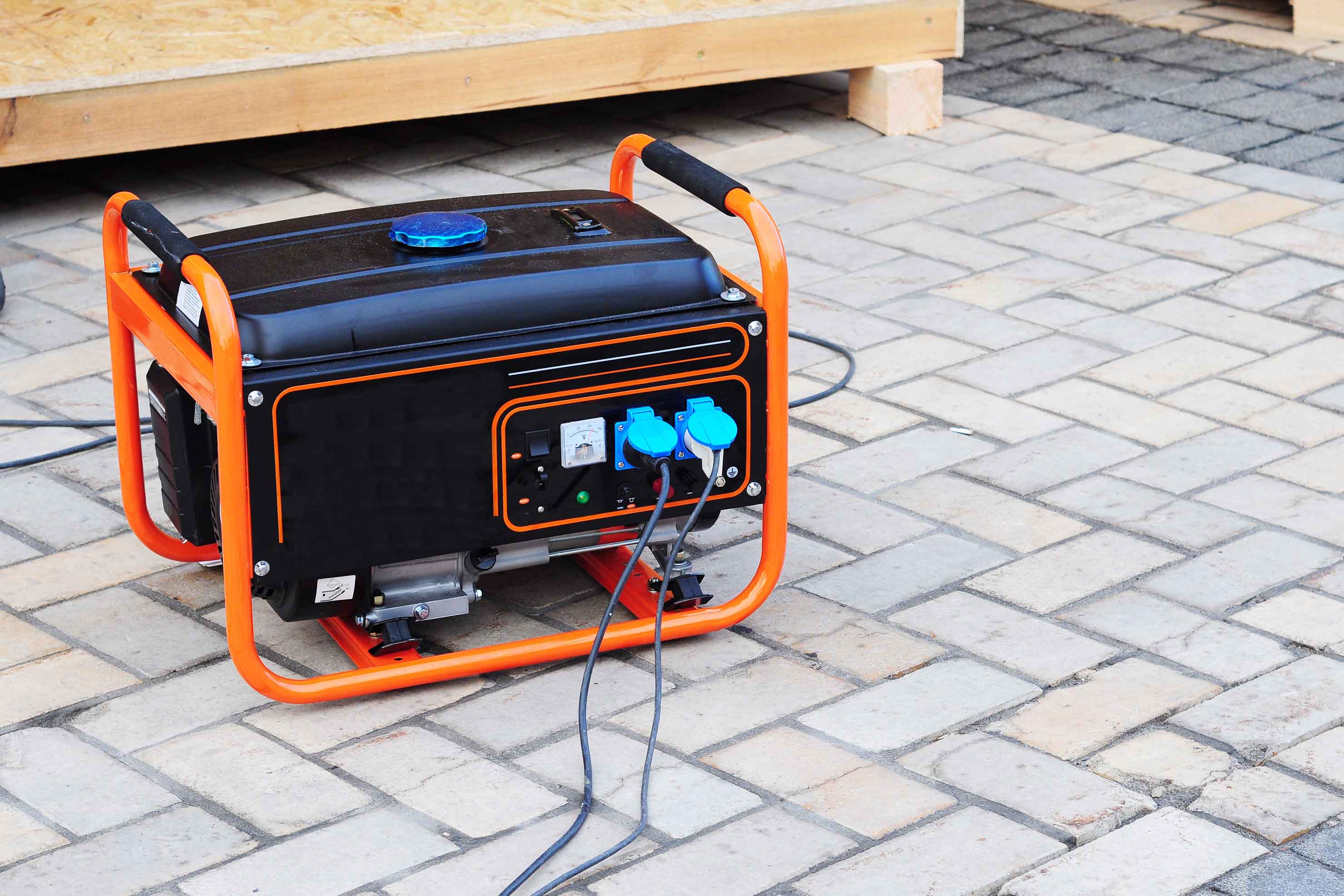

Portable Generators
Portable Generators are a great choice for those who need a reliable source of power without the permanent installation of a standby generator. Portable generators are available in a variety of sizes, from small to large, and can be powered by gasoline, diesel, or propane. They are also great for camping, tailgating, or other outdoor activities.
Standby Generators
Standby generators are designed to provide a continuous power source to your home or business. These generators are generally larger and more powerful than portable generators and are permanently installed in a designated area, such as a garage or shed. Standby generators are powered by natural gas or propane and can provide backup power in the event of a power outage.
Inverter Generators
Inverter generators are designed to provide a clean, steady source of power. They are smaller and lighter than traditional portable generators, making them a great choice for camping or other outdoor activities. Inverter generators use advanced inverter technology to provide clean, quiet power that is ideal for powering sensitive electronic devices.
Generator Power Ratings
Generator power ratings are the standards used to measure the output of a generator. Generators are rated in watts or kilowatts (kW) and are determined based on the amount of energy they can produce over a certain period of time. Generator power ratings also include voltage, current and frequency ratings.
Generators are rated by their maximum output power. This is the maximum amount of power the generator can produce. When selecting a generator, it is important to choose one that is rated to meet the power needs of the application.
| Rating | Description |
|---|---|
| Voltage | The maximum voltage the generator can safely output |
| Current | The maximum current the generator can safely output |
| Frequency | The frequency of the alternating current produced by the generator |
| Power | The maximum amount of power the generator can produce |
The power rating of a generator is determined by the manufacturer, and it is important to read and understand the manufacturer’s specifications to ensure the generator is capable of providing the power required. It is also important to consider the generator’s efficiency and noise levels when selecting a generator.
Generator Power Output
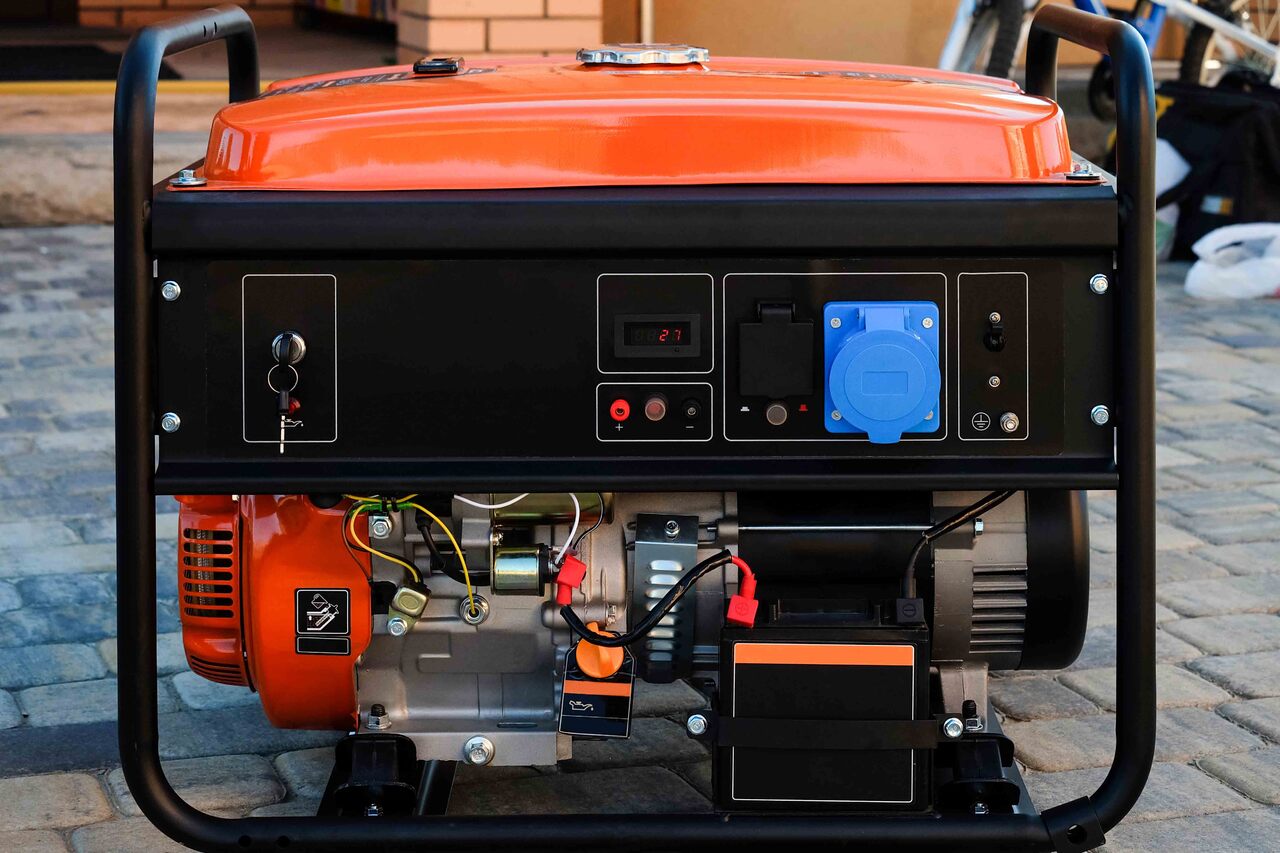

Generators are powerful pieces of equipment that can provide a dependable source of electricity. They are used in a variety of circumstances, from providing emergency power to home and businesses to powering outdoor events and construction sites. The amount of power generated by a generator depends on several factors, including its size and type.
- Gasoline Generators – These are the smallest and least powerful generators, typically producing between 1,000 and 6,000 watts of power. Smaller models are ideal for camping and tailgating, while larger models may be used to power small appliances and tools.
- Diesel Generators – Diesel generators produce between 8,000 and 15,000 watts of power and are used to power larger appliances, tools, and machinery.
- Natural Gas Generators – Natural gas generators are the most powerful types of generators, producing up to 25,000 watts of power. These generators are used to power large construction sites and industrial facilities.
No matter the type of generator, it is important to ensure that it is sized correctly for the job. Overloading a generator can lead to damage to the generator and the equipment it is powering. It is also important to ensure that the generator is properly maintained to ensure it is running efficiently and safely.
Generator Safety and Maintenance
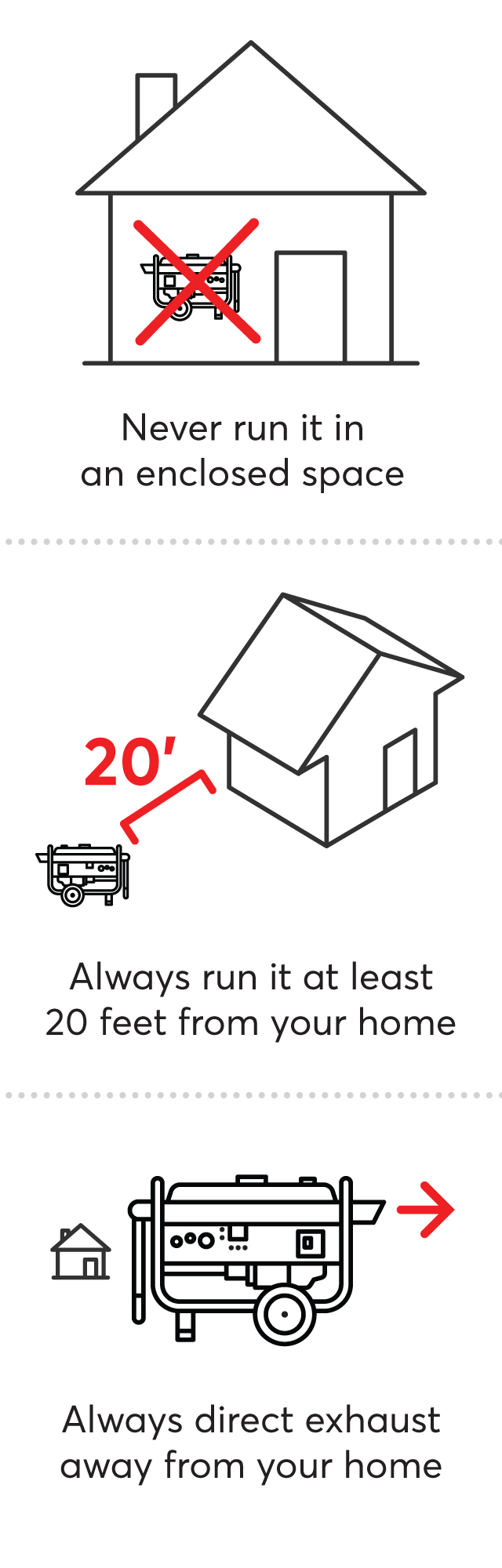
Generator safety and maintenance are essential to ensure the safe and efficient operation of your generator. Proper generator maintenance and safety procedures will help to ensure that your generator will provide reliable power when needed.
Generator safety begins with the basic safety precautions of electrical wiring, use of extension cords and circuit breakers, and proper grounding of any components. All of these safety measures should be taken before any generator is used.
It is also important to keep the generator in good working order. Regular maintenance should include changing the oil, inspecting and cleaning the air filter, replacing spark plugs, and checking the battery level.
It is also important to inspect the generator for signs of wear and tear, such as cracked wiring or connectors, corrosion, and signs of overloading. If any of these signs are present, the generator should be taken in for repair immediately.
When the generator is not in use, it should be stored in a dry, ventilated area and covered with a weatherproof cover. This will help to protect the generator from the elements and reduce the risk of fire.
| Maintenance Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Change Oil | Every 3 Months |
| Inspect & Clean Air Filter | Every 6 Months |
| Replace Spark Plugs | Every 12 Months |
| Check Battery Level | Every 6 Months |
Finally, always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for operating the generator and keep the generator away from flammable materials. Also, only use the generator outdoors and never use it in an enclosed space.
By following these safety and maintenance tips, you can ensure that your generator will provide reliable power when you need it.
Generator Fuel Types

Generators are available in various fuel types such as gasoline, diesel, natural gas, propane, and even solar. Each fuel type has its own advantages and disadvantages. Below is a comparison of the different generator fuel types.
| Fuel Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Gasoline | Easy to find, low cost, and easy to store | Loud and polluting |
| Diesel | High efficiency and long-lasting | More expensive and more difficult to store |
| Natural Gas | Low cost, clean burning, and easy to store | Not available in most areas |
| Propane | Clean burning, easy to store, and reliable | Expensive and not available in most areas |
| Solar | Clean and renewable energy source | Expensive and dependent on weather conditions |
The type of fuel you choose for your generator will depend on your budget, location, and power needs. Be sure to do your research before purchasing a generator to make sure you get the right one for your needs.
Generator Noise Levels

The amount of noise produced by a generator depends on several factors, including the size and type of the machine, the type of fuel used, and the load it is carrying. Generators are generally rated according to their decibel levels. A decibel (dB) is a unit used to measure the intensity of sound.
Generators can produce noise levels ranging from 45 dB to over 100 dB, depending on the size and type of the machine. Small, portable generators are typically quieter than larger, stationary generators, and gasoline-powered models typically produce more noise than diesel-powered models.
When operating a generator, it is important to consider the noise levels to ensure that the noise is not disruptive to the surrounding environment. A generator producing more than 85 dB of noise is considered to be excessively loud and can cause hearing damage if operated for a prolonged period of time.
| Generator Type | Noise Level (dB) |
|---|---|
| Small, Portable | 45-60 |
| Large, Stationary | 60-85 |
| Gasoline-Powered | 75-85 |
| Diesel-Powered | 60-75 |
Generator Cost
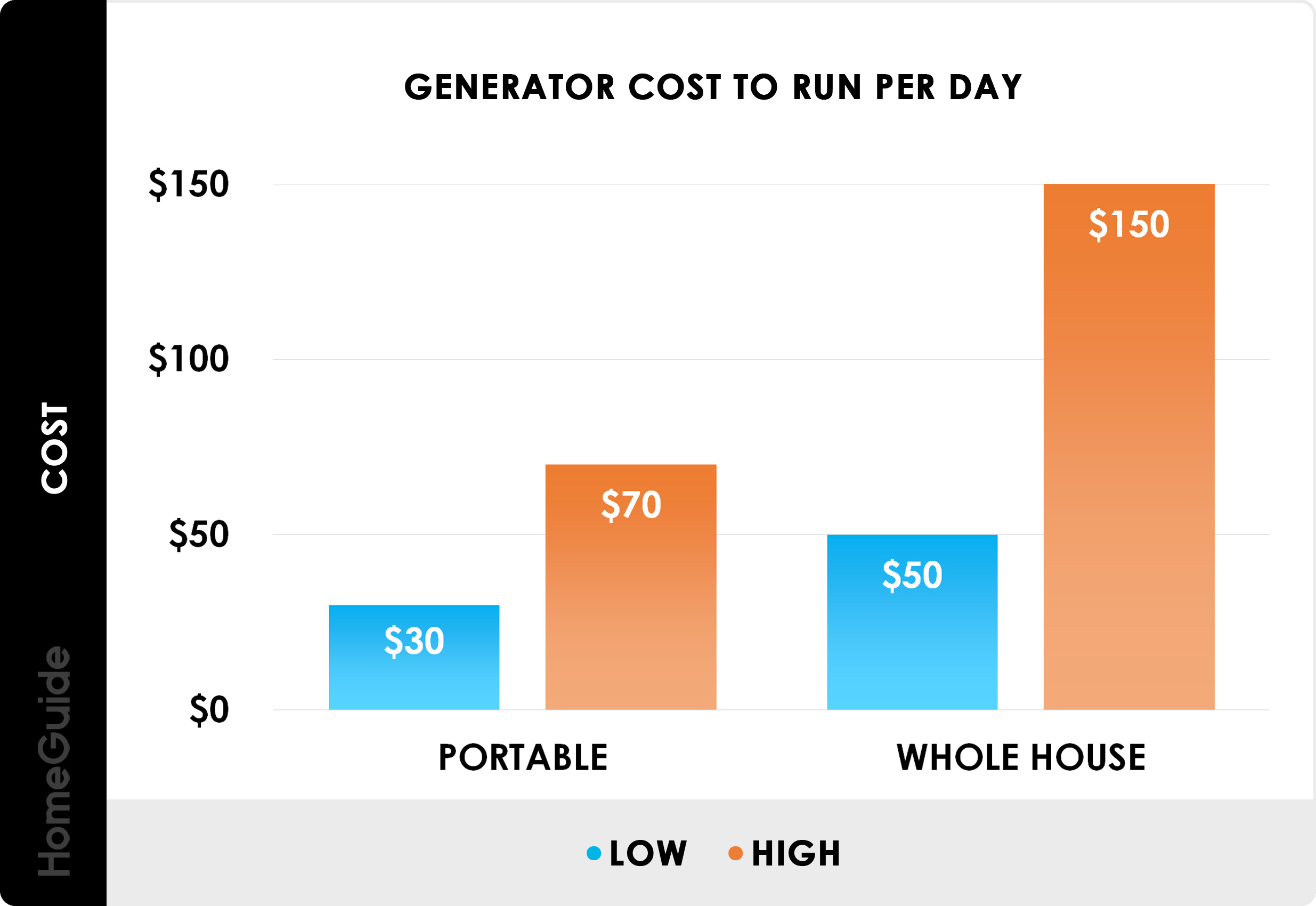
When it comes to generator power, the cost of the generator can be a major consideration. Generators can range from very small and affordable to large and expensive. For those on a budget, a small generator that produces enough power to run a few appliances or light a few rooms can be a great option. For those with larger power needs, a larger generator with more power output can be necessary.
The cost of a generator can be broken down into three main components: initial cost, fuel cost, and maintenance cost. The initial cost of a generator depends largely on its size and power output. Larger generators will naturally cost more initially, but may be more cost effective in the long run. Fuel cost is dependent on the type of fuel the generator uses and the amount of power it requires to run. The cost of fuel for generators can vary based on the type of fuel and how much power is needed. Maintenance cost is the cost of regular maintenance for the generator. This includes things like oil changes and filter replacements, as well as repairs if necessary.
When considering the cost of a generator, it’s important to weigh the initial cost, fuel cost, and maintenance cost against the benefits of having a generator. Generators can provide power in areas where it’s not readily available, and can save money in the long run if they are properly maintained. By weighing the cost and benefits, you can make an informed decision on the best generator for your needs.
Generator Reviews
When it comes to finding the right generator for your needs, there is no substitute for reading generator reviews from those who have already purchased and used the equipment. Doing the research and reading the reviews can give potential buyers an idea of the quality of the generator, the features it offers, and the overall satisfaction level of the people who bought it.
Generator reviews can be found on a variety of websites, including consumer review sites such as Consumer Reports and websites dedicated to generators. These reviews can provide a wealth of information, including how easy the generator is to use and maintain, how reliable it is, how quiet it runs, and how much power it can generate.
When reading reviews, it’s important to keep in mind that different individuals have different needs and expectations when it comes to generators. Some people may be looking for a generator that is very reliable, while others may be looking for something that is more affordable. It’s important to read reviews from people who have similar needs and expectations as your own.
In addition to reading reviews, it’s also important to compare different generators and their features. It’s a good idea to research the size, power output, fuel efficiency, and other features before making a final decision. This will ensure that the generator you purchase is the best fit for your needs.
Generator reviews can be a valuable resource for anyone looking to purchase a generator. By doing research and reading reviews, potential buyers can get an idea of the quality and features of a generator, as well as the overall satisfaction level of those who have used it. This can help them make an informed decision and get the best generator for their needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the different types of electric power generators?
Electric power generators are an important source of electricity, providing a reliable and clean energy source. Generators can be divided into two main categories: stationary and portable.
Stationary Electric Power Generators
Stationary generators are large and powerful machines designed to produce electricity for a long time. They are usually used in industrial areas, power plants, and other large facilities. The most common types of stationary generators are:
- Gasoline Generators – These are powered by gasoline and are usually used in emergency situations where access to electricity is limited.
- Diesel Generators – These run on diesel fuel and are typically used in industrial areas, where they are more efficient than gasoline-powered generators.
- Natural Gas Generators – These are powered by natural gas and are generally used in areas where natural gas is readily available.
- Steam Turbine Generators – These are powered by steam and are used in power plants and other large industrial facilities.
- Nuclear Generators – These are powered by nuclear fission and are used in nuclear power plants.
Portable Electric Power Generators
Portable generators are smaller and less powerful than stationary generators. They are usually used in recreational areas, such as camping sites, or in emergency situations. The most common types of portable generators are:
- Diesel Generators – These run on diesel fuel and are usually used in recreational areas, such as camping sites, or in emergency situations.
- Gasoline Generators – These are powered by gasoline and are often used in recreational areas or in emergency situations.
- Solar Generators – These are powered by solar energy and are usually used in recreational areas, such as camping sites.
2. How do I choose an electric generator power?
When it comes to choosing the right electric generator power for your needs, there are several important factors to consider.
- The first and most important factor is the type of power source you will be using. Depending on your needs, you may need to choose between gas, diesel, or propane. Each type of power source has its own advantages and disadvantages.
- The second factor to consider is the wattage of the generator. This will determine how much power your generator can provide. It is important to choose a generator that can provide enough power for your needs.
- The third factor to consider is the size of the generator. The larger the generator, the more power it can provide. It is important to choose a generator that is the right size for your needs.
- The fourth factor to consider is the noise level of the generator. Some generators can be very loud and it is important to choose a generator that is quiet enough for your needs.
- The fifth factor to consider is the cost. Generators can range in price from a few hundred dollars to several thousand dollars, depending on the size, wattage, and power source. It is important to choose a generator that fits your budget.
Once you have considered all of these factors, you will be able to choose the right electric generator power for your needs.
3. What is the difference between an electric, electronic and eletric generator?
Generators can be divided into three main types: electric, electronic, and electric generators. Each type of generator has its own unique advantages and disadvantages. This section will discuss the differences between the three types of generators.
- Electric Generators are the most common type of generator, and they are used to produce electricity. They are powered by either an internal combustion engine or a steam turbine. Electric generators can be used to power anything from a small appliance to an entire home.
- Electronic Generators are designed to generate higher frequencies than electric generators. They are used mainly in industrial and commercial applications, such as powering industrial motors, machines, and other equipment. They are also used in audio equipment and some medical applications.
- Eletric Generators are designed to produce alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC). They are typically used in large-scale applications, such as powering an entire home or an industrial plant. They are powered by either electricity or fuel, and can be used for both residential and commercial purposes.
These are the main differences between electric, electronic, and electric generators. Each type of generator has its own unique advantages and disadvantages, so it is important to consider these factors when deciding which type of generator is best for your needs.
4. What are the advantages of using a generator?
- Generators are a reliable and efficient way to provide electricity. They provide a backup source of power and can be used to supply power during an outage or emergency.
- Generators are portable, so they can be used in different locations and can be moved as needed.
- Generators are relatively inexpensive and easy to install and operate.
- Generators come in many different sizes and can be used to power small appliances or large industrial machines.
- Generators are safe to use and can be used to power sensitive equipment.
- Generators can be used to supplement existing power sources or to provide additional power when needed.
5. What are the Best Practices for Using an Electric Generator?
- Make sure the generator is properly grounded.
- Read the manual and familiarize yourself with the generator before use.
- Check the oil level in the generator and refill it if necessary.
- Ensure that the generator is connected to an appropriate power source.
- Use a surge protector or UPS to protect connected devices.
- Do not overload the generator by connecting too many devices.
- Keep the generator in a well-ventilated area.
- Regularly inspect the generator for any damages or wear and tear.
- Store the generator in a dry place when not in use.
Conclusion
Generators are a powerful tool for home and business owners. They can provide power during unexpected outages, and they can be used to help reduce energy costs. By using reviews and guides, people can make an informed decision when it comes to buying a generator. When purchasing a generator, it is important to consider the size and type of generator needed, as well as any safety features that may be necessary. With the right generator, people can enjoy the benefits of reliable power and energy savings.
References
- AC Electrical Generators – Basics. (2016). Retrieved from https://www.allaboutcircuits.com/textbook/alternating-current/chpt-9/ac-electrical-generators-basics/
- Generator Reviews. (2016). Retrieved from https://www.consumerreports.org/cro/generators/buying-guide.htm
- Generator Guide – How to Buy a Generator. (2016). Retrieved from https://www.homeadvisor.com/r/buying-a-generator/
- Generator Buying Guide. (2016). Retrieved from https://www.lowes.com/projects/repair-and-maintain/generator-buying-guide/project






