Generators and inverters are two essential pieces of equipment that are important for any home, business, or recreational activity. Generators provide power when the electricity is out while inverters provide power when a different type of electricity is needed. In this article, we will explore the differences between generators and inverters, review the best products on the market, and provide helpful guides for how to use and maintain them. Read on to learn all you need to know about generators and inverters.
What is a Generator?

A generator is an electrical device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. It uses a rotating magnetic field to generate an electric current in the form of alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC). Generators are used in a variety of applications, from powering small appliances in the home to providing power for large industrial facilities.
Generators are typically powered by gasoline, diesel, natural gas or propane, though some are powered by wind or solar energy. They come in a variety of sizes, ranging from small, portable models to large, industrial-sized generators.
Generators can be divided into two main categories – synchronous and asynchronous. Synchronous generators use a rotating magnetic field to directly produce electricity, while asynchronous generators use an engine or turbine to mechanically produce electricity.
| Generator Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Synchronous Generator | Directly produces electricity using a rotating magnetic field. |
| Asynchronous Generator | Mechanically produces electricity using an engine or turbine. |
Generators are an important part of many homes and businesses, providing an essential backup source of power in the event of an electrical power outage. They are also used in many industrial and commercial applications, providing a reliable source of power for heavy machinery and equipment.
What is an Inverter?

An inverter is a device that converts direct current (DC) electricity into alternating current (AC) electricity. It is a type of electrical power converter that changes the voltage and frequency of the electricity to match the availability of the local electricity grid. Inverters are commonly used in applications such as:
- Residential solar panel systems
- UPS systems
- Solar-powered water pumps
- Wind turbines
- Hybrid and electric vehicles
Inverters are designed to transform DC power from a battery, solar panel or wind turbine into AC power. The AC power can then be used to power appliances, such as lights, air conditioners, refrigerators, televisions, and other household devices. Inverters are available in a variety of sizes and power ratings, and can be used for both residential and commercial applications.
Generator vs Inverter – Comparison

1 Pros and Cons of Generators
Generators are a popular choice for providing power in remote locations, or in the event of a power outage. They provide a reliable source of power and can be used in a variety of applications. However, generators have some drawbacks, such as noise and fuel consumption.
2 Pros and Cons of Inverters
Inverters are a newer technology that converts direct current (DC) electric power to alternating current (AC) electric power. Inverters are much quieter than generators, and they consume less fuel. However, they are more expensive and require more maintenance than generators.
Considerations for Choosing a Generator or Inverter
When deciding whether to purchase a generator or an inverter, it is important to consider several factors. The following list outlines some of the key considerations to keep in mind when making your choice:
- Power Output: Determine the power output needs of the equipment you plan to power and select a generator or inverter that will meet these needs.
- Size: Consider the size of the generator or inverter compared to the space available. Ensure the size you choose will fit in the space you have.
- Fuel Type: Consider the fuel type the generator or inverter uses. Select a type that is easily available and cost effective.
- Noise Levels: Check the noise levels of the generator or inverter you are considering. Noise levels can be an important consideration in residential areas.
- Cost: Consider the cost of the generator or inverter. Determine how much you can afford to spend and select a model that will fit into your budget.
- Maintenance: Determine how much maintenance the generator or inverter requires and how often it must be done. Ensure you have the time and resources to complete the maintenance.
By taking the time to consider all of these factors, you will be able to select the best generator or inverter for your needs.
Best Practices for Using Generators or Inverters

Generators and inverters are essential pieces of equipment for many businesses, but it is important to use them correctly for the best results. To ensure that you get the most out of your generator or inverter, here are some best practices to follow:
- Always read the manufacturer’s manual before operating your generator or inverter.
- Make sure the generator or inverter is properly installed and located in an area that is free from combustible materials.
- Keep the generator or inverter clean and in good working order. Regular maintenance will help ensure that it runs safely and efficiently.
- Inspect the generator or inverter for any signs of damage or wear before each use.
- Only use fuel that is approved by the manufacturer for your generator or inverter.
- Make sure the generator or inverter is connected to a properly grounded outlet.
- If necessary, install a surge protector to protect the generator or inverter from voltage spikes or power surges.
- If you are using an inverter, make sure it is properly sized for your needs.
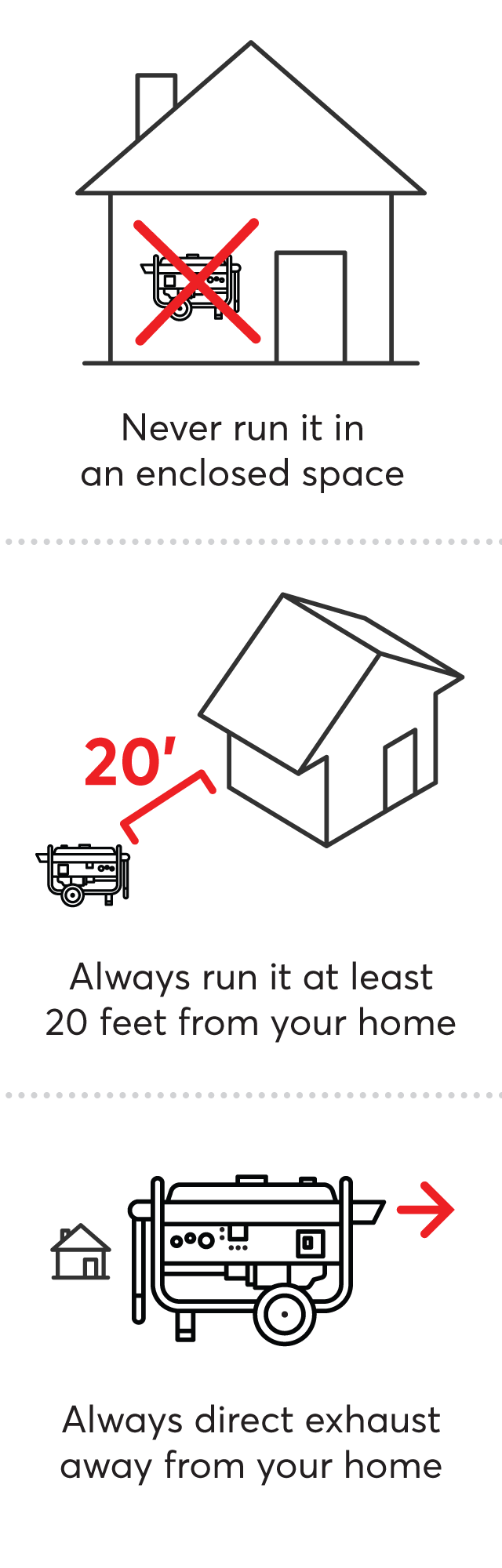
- Never operate a generator or inverter in an enclosed area.
- Allow the generator or inverter to cool down before refueling it.
- Always store the generator or inverter with a full tank of fuel.
- Never overload the generator or inverter.
By following these best practices for using generators or inverters, you can ensure that your equipment runs safely and efficiently. If you have any questions about using your generator or inverter, you should contact the manufacturer for further instructions.
Safety Tips for Using Generators or Inverters

Generators and inverters are powerful tools that can provide you with electricity when you don’t have access to a power grid. However, they come with their own safety risks and should be handled with caution. Here are some tips to help you stay safe when operating a generator or inverter:
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Read the Manual | Before using a generator or inverter, be sure to read the instruction manual and follow all safety precautions. |
| Use Outdoors Only | Generators and inverters should only be used outdoors in a well-ventilated area, away from windows, doors, and ventilation intakes. |
| Use a Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter | A ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) should be used to protect against electric shock. It should be installed in any outlet used to power the generator or inverter. |
| Check for Leaks | Make sure there are no fuel, oil, or coolant leaks before operating the generator or inverter. |
| Keep Away From Children | Keep children away from the generator or inverter at all times. Do not allow them to operate the equipment. |
| Use Protective Gear | When operating the generator or inverter, wear protective gear such as gloves, goggles, and ear protection. |
Following these tips will help you stay safe when using a generator or inverter. Remember, generators and inverters are powerful tools that should be used with caution.
Generator or Inverter Maintenance
Maintaining your generator or inverter is key to maximizing its performance and extending its lifespan. Regular maintenance can help you avoid costly repairs or replacements down the road. Here are some tips for keeping your generator or inverter in top condition:
1. Inspect the generator or inverter regularly, to make sure it is in good working condition. Check for any signs of wear and tear, and replace any broken or worn parts as soon as possible.
2. Clean the generator or inverter regularly. Dirt and debris can accumulate over time, which can lead to issues with the performance of the generator or inverter.
3. Make sure the generator or inverter is adequately lubricated. This will help to ensure that all the moving parts are running smoothly.
4. Check the fuel lines and filters on a regular basis. Replace any filters that are clogged, and make sure all fuel lines are free of blockages or leaks.
5. Check the battery connections and terminals. If the connections are loose or corroded, they should be cleaned and tightened.
6. Make sure the generator or inverter is in a safe and secure location. It should be protected from the elements, and away from any combustible materials.
7. Test the generator or inverter regularly to make sure it is working properly.
By following these simple maintenance tips, you can help to ensure that your generator or inverter continues to operate in peak condition. Regular maintenance can help to extend the lifespan of your generator or inverter, and minimize the need for costly repairs or replacements.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between a generator and an inverter?
A generator and an inverter are both types of power sources that are used to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, but they serve two different purposes. Here is a brief comparison of the two:
- Generator: A generator is a device that is used to produce electrical energy from mechanical energy. It is typically powered by an internal combustion engine, and it can be used to provide electricity to a variety of applications, including homes, businesses, and recreational vehicles.
- Inverter: An inverter, on the other hand, is a device that is used to convert direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). It is usually powered by a battery, and it is commonly used to provide power for appliances and electronic devices.
In summary, a generator is used to produce electrical energy from mechanical energy, while an inverter is used to convert direct current into alternating current.
2. How does an inverter generator work?
An inverter generator is a type of generator that produces a clean, stable power output with minimal fluctuations. Unlike conventional generators, inverter generators use technology to regulate the output voltage, allowing them to produce a more reliable power supply.
- The inverter generator uses an electrical circuit to convert the direct current (DC) generated by the engine to an alternating current (AC).
- The AC output is then passed through a series of transformers and filters, which cleans the power, removing any spikes or dips in the voltage.
- The power is then passed through an inverter, which further regulates the voltage, ensuring that the AC output is always stable.
- The clean, stable power is then passed to the generator’s outlets, ready to be used.
Inverter generators are particularly useful for powering sensitive electronics, as the clean power output ensures that there are no surges or dips in voltage, which can damage delicate equipment.
3. What are the advantages of an inverter generator over a regular generator?
Inverter generators offer a number of advantages over regular generators, making them a popular option for many applications. Here are some of the main benefits of using an inverter generator:
- Quiet operation: Inverter generators are designed to run more quietly than regular generators, allowing you to use them in areas where noise pollution could be an issue.
- Fuel efficiency: Inverter generators are more fuel-efficient than regular generators, so they can run longer on the same amount of fuel.
- Portability: Inverter generators are typically smaller and lighter than regular generators, making them easier to transport and store.
- Produce cleaner power: Inverter generators produce cleaner power than regular generators, making them better for sensitive electronics.
- Cost: Inverter generators are generally more expensive than regular generators, but they offer better performance and longer life.
4. What are the benefits of a Power Inverter Generator System?
Power inverter generators provide numerous benefits, which include:
- Quiet operation: An inverter generator runs at a much lower decibel level than a conventional generator, making it ideal for camping, tailgating, and other outdoor activities.
- High efficiency: Inverter generators are able to convert their fuel into electricity with much higher efficiency than traditional generators.
- Cleaner power: Inverter generators produce cleaner power than traditional generators and are much less harmful to sensitive electronics.
- Portability: Inverter generators are much lighter and more compact than traditional generators, making them easy to transport and store.
- Fuel economy: Inverter generators are able to switch to a low-power mode when they are not running at full capacity, which helps to conserve fuel.
5. What is the best option between a generator and an inverter generator?
When choosing between a generator and an inverter generator, it is important to consider the purpose and environment in which the generator will be used.
- Generators: Generators are a great choice for powering larger appliances such as water pumps, and provide reliable, cost-effective power for remote locations. Generators are often less expensive than inverter generators, but they are not as efficient, and the fuel they use is often more polluting.
- Inverter Generators: Inverter generators are a great choice for powering sensitive electronics, as they produce clean, consistent power. They are more expensive than generators, but they are more efficient and quieter, making them ideal for recreational use.
Ultimately, the best option between a generator and an inverter generator depends on the purpose and environment in which the generator will be used. For larger appliances, a generator may be the most cost-effective option, while an inverter generator may be a better choice for recreational use.
Conclusion
Generators and inverters are two important components of any power system. Generators are typically used to provide primary power to the system, while inverters can be used to provide backup power. Generators and inverters can be used together to create a hybrid system that is both reliable and efficient.
When deciding between a generator or inverter, it’s important to consider your particular needs and the environment in which the system will be used. Different types of generators and inverters can provide different levels of power and efficiency, so it’s important to compare and evaluate the different options before making a decision.
Generator and inverter reviews can help you make an informed decision, as can guides and tutorials that provide more detailed information about the different components of a power system. Ultimately, the best way to know if a generator or inverter is right for you is to research and experiment to find the best power solution for your needs.
References
- Bryant, A. (2018, June 28). What is a Generator and How Does it Work? Retrieved from https://www.generatorjoe.net/understanding-generators/
- Dziedzic, M. (2020, April 10). Generator vs. Inverter: What’s the Difference? Retrieved from https://www.homedepot.com/c/ah/generator-vs-inverter-whats-the-difference/9ba683603be9fa5395fab905c2f1d2a4
- Eaton, E. (2019, January 24). Generator Reviews – Best Generators. Retrieved from https://generatorgrid.com/reviews/
- Generac Power Systems. (2020). Generator Buying Guide. Retrieved from https://www.generac.com/home/support/buying-guides/generator-buying-guide
- Generator Place. (2020). How to Choose a Generator. Retrieved from https://www.generatorplace.com.au/blog/how-to-choose-a-generator/
- Honda Generators. (2020). What to Consider When Shopping for a Generator. Retrieved from https://powerequipment.honda.com/generators/types-of-generators/what-to-consider-when-shopping-for-a-generator
- Houle, M. (2018, August 11). Best Generator Reviews – Consumer Reports. Retrieved from https://www.consumerreports.org/cro/generators/buying-guide






