Generators are a handy and essential tool for many people, providing a reliable source of power when needed. This article will provide an introduction to generators, including reviews, guides, and how to use them. You’ll learn how to choose the right generator, what to look for when buying one, and how to properly maintain it. We’ll also provide advice on how to get the most out of your generator. So read on and get ready to power up!
Definition of a Generator

A generator is an electrical device that produces an alternating electric current. Generators are used in many different applications, from supplying electricity to homes and businesses to providing power for industrial machinery. Generally, generators consist of an engine connected to a rotating armature that produces electrical current when the engine is running. Generators are typically powered by gasoline, diesel, natural gas, or other fuels.
Generators are also used to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. This is done by using a device called an alternator, which is a type of generator. The alternator produces alternating current by using magnets and a rotating field to create an electrical field. This electrical field is then used to generate electricity.
Generators are also used in the production of electricity, such as in power plants. In these plants, generators are used to convert mechanical energy, such as steam or wind, into electrical energy. Generators are also used to provide backup power in case of a power failure or emergency.
Generators can be used for a variety of purposes, from providing electricity to powering machinery. They are an important part of any electrical system and are used in many different industries.
What are Generators Used For?

Generators are devices used to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. They are used to generate electricity for a variety of applications, from home appliances and industrial machinery to large-scale power plants. Generators are used to produce electricity from a variety of fuel sources, including fossil fuels, such as coal and natural gas, and renewable sources, such as wind and solar power.
Generators are used in a variety of ways, depending on the application. For home use, they are typically used to provide backup power in the event of a power outage, or to provide electricity to remote locations not connected to the grid. In industrial and commercial settings, they are often used as a source of emergency power or as a way to supplement the grid during times of peak demand.
Generators are also used to provide power for large-scale projects, such as construction sites or special events. They can also be used to provide power to remote areas, such as agricultural or mining sites, where access to the grid is not available. As technology advances, they are increasingly used to store energy generated from renewable sources, such as wind and solar, for use during times of peak demand.
Generators are an essential part of our modern lives and can be found in a variety of applications. From powering our homes, businesses, and industries to providing remote power to rural areas, generators are an important tool for ensuring reliable electricity is available when and where it’s needed.
Types of Generators

Generators are machines that produce electrical energy. There are several types of generators, each of which is used for specific applications. The types of generators include:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Portable Generators | Portable generators are small, lightweight, and easy to transport. They are used for powering small appliances and tools, such as camping equipment and lawnmowers. |
| Standby Generators | Standby generators are larger and more powerful than portable generators. They are used in industrial and commercial settings to provide backup power in case of a power outage. |
| Turbine Generators | Turbine generators are large-scale generators used to produce electricity from sources such as wind, water, and geothermal energy. |
| Solar Generators | Solar generators use solar panels to convert solar energy into electricity. They are used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. |
| Hydro Generators | Hydro generators use the power of falling water to produce electricity. They are used in dams and other large-scale projects. |
Each type of generator has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the type of generator chosen will depend on the specific application. The best way to find the right generator is to consult with an experienced technician who can help you select the generator that best suits your needs.
History of Generators

Generators have been around since the late 1800s, and have been used in a variety of applications over the years. Here is a brief overview of the history of generators:
- The first generator was developed in 1872 by Zénobe Gramme, a Belgian inventor. It was the first commercial generator and generated direct current (DC) electricity.
- In the early 1900s, Nikola Tesla developed the first alternating current (AC) generator, which was more efficient than DC generators.
- In the 1920s, the first diesel-powered generators were developed. These generators were used in a variety of applications, including powering ships, factories, and remote locations.
- In the 1940s, diesel-powered generators became more sophisticated, and were used to generate electricity for households.
- In the 1950s and 1960s, the development of the transistor revolutionized the generator industry. Transistors allowed for the development of smaller and more efficient generators.
- In the 1970s, the development of microprocessors further advanced generator technology. Generators were able to become even smaller, more efficient, and more reliable.
- Today, generators are used in a variety of applications, from providing backup power for homes and businesses to powering remote locations. They are available in a variety of sizes and types, from small portable generators to large industrial generators.
The First Generator

The first generator was invented in 1832 by Michael Faraday. This invention was revolutionary in its time, allowing for the conversion of mechanical energy into electrical energy. It marked the beginning of the modern era of electricity.
Faraday’s invention worked by using a coil of wire and a magnet to create an electric current. The coil of wire was placed inside a magnetic field, where the motion of the coil caused the magnetic field to induce an electric current. This principle, known as electromagnetic induction, is still used in modern generators today.
Faraday’s invention was used to power the first electric light bulb and was the foundation for the development of the electric motor. It also paved the way for the development of the alternating current (AC) generator, which is the basis for the generation of electricity used in homes and businesses today.
| Name | Inventor | Year Invented |
|---|---|---|
| First Generator | Michael Faraday | 1832 |
How Generators Work
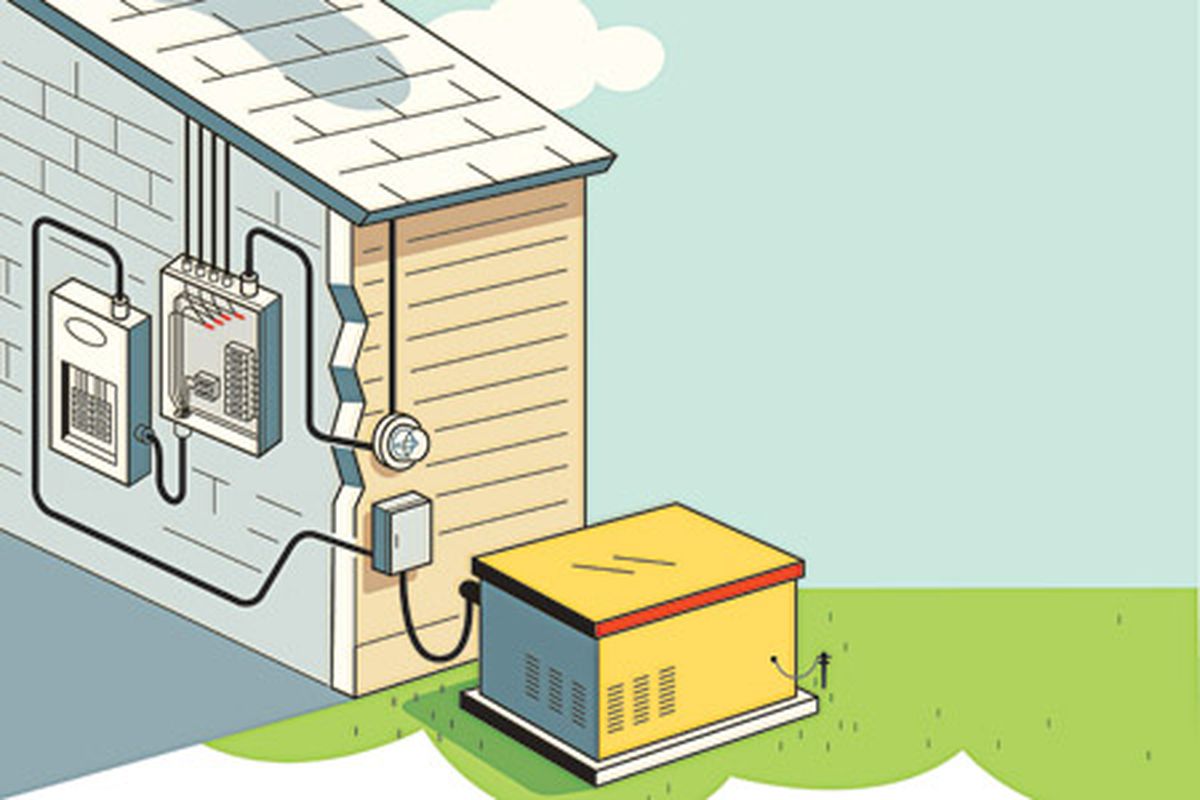
Generators are machines that produce electrical energy from mechanical energy. They are used to provide power to electrical devices for a variety of applications, from powering homes and businesses to providing backup power in the event of a power outage.
Generators work by converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. This is done through a process called electromagnetic induction. The basic components of a generator are the stator, rotor, and armature.
- The stator is the stationary part of the generator and is usually made of copper windings.
- The rotor is the rotating part of the generator and is usually made of a metal wheel.
- The armature is the part that connects the stator and rotor and is usually made of magnets.
When the rotor is rotated, it creates a magnetic field which induces a current in the stator. This current is then passed through the armature which creates an alternating current (AC) that can be used to power electrical devices.
Generators can be powered by a variety of sources, including gasoline, diesel, and natural gas. In addition to providing power for homes and businesses, generators are also used to provide power for medical equipment, emergency lighting, and other applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Generators

Generators are a great source of electricity for home and industrial uses. They are reliable, efficient, and portable, making them an ideal choice for many applications. However, there are some advantages and disadvantages of using generators that should be considered before investing in one.
Advantages of Generators
Generators are a very reliable source of electricity. They are capable of producing electricity even in areas where the main power supply is unreliable or unavailable. Generators are also efficient, as they can produce electricity that is of the same quality and voltage as the mains power. They are also portable, making them easy to transport and deploy in different locations.
Generators can also provide emergency power in the event of a power outage. This is especially useful for businesses, as it can help to keep the operations running in times of emergency.
Finally, generators are relatively inexpensive to purchase and operate. This makes them an attractive option for many people.
Disadvantages of Generators
Generators are not without their drawbacks. Generators require regular maintenance, as they need to be refueled and serviced regularly. This can be costly and time-consuming.
Generators also produce noise, which can be disruptive and annoying. Additionally, they can produce dangerous levels of carbon monoxide, which can be hazardous to health.
Finally, generators require periodic testing and inspection to ensure they are functioning properly. This is an additional cost that must be taken into consideration when investing in a generator.
Conclusion
Generators are a great source of electricity, and they can be used in a variety of situations. However, it is important to weigh the advantages and disadvantages of generators before investing in one. With proper research and maintenance, a generator can be a reliable and cost-effective source of power.
Generator Maintenance
Maintaining your generator is essential to ensure it runs smoothly and efficiently. To keep your generator in good working condition, you should perform regular maintenance tasks such as changing the oil, checking the air filter, inspecting the spark plugs and cleaning the carburetor.
Changing the Oil
It is important to change the oil in your generator on a regular basis. Oil changes should be done at least once a year or every 100 hours of use. To change the oil, you will need to drain the old oil into a container and replace it with new oil.
Checking the Air Filter
The air filter should be checked regularly to ensure it is free of dust, dirt, and debris. If the air filter is dirty, it can reduce the efficiency of the generator. The air filter should be replaced every 6 months or 500 hours of use.
Inspecting the Spark Plugs
The spark plugs should be inspected every 6 months or 500 hours of use. Inspecting the spark plugs will help identify any potential problems with the generator.
Cleaning the Carburetor
The carburetor should be cleaned periodically to ensure it is free of debris and buildup. This can be done using a carburetor cleaner, which is available at most auto parts stores.
Additional Maintenance Tips
| Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Check the cooling system | Every 6 months or 500 hours of use |
| Check the fuel system | Every 6 months or 500 hours of use |
| Check the electrical system | Every 6 months or 500 hours of use |
| Check the belts and hoses | Every 6 months or 500 hours of use |
Following these generator maintenance tips will help keep your generator running smoothly and efficiently. It is also important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for maintenance and repair.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is a generator and how does it work?
A generator is an electrical device that produces an alternating current (AC) by converting mechanical energy from a fuel source such as gasoline, diesel, or natural gas. Generators are commonly used to provide power to residential and commercial buildings, as well as industrial and agricultural operations.
Generators convert mechanical energy into electrical energy by using an internal combustion engine, or by tapping into an external energy source such as a turbine or water wheel. The engine or external energy source is connected to a generator head, which contains coils of wire wrapped around magnets. The movement of the coils of wire within the magnets creates a magnetic field, which produces electrical energy when the generator is turned on.
Generators produce AC electricity, which is then sent through a transfer switch to an inverter that converts the AC electricity into a direct current (DC) power source. The DC power is then sent to the home, commercial building, or industrial operation to power the necessary appliances and equipment.
Generators are available in a variety of sizes and power outputs to meet the needs of any application. The size of the generator is determined by the amount of power needed to supply the appliances or equipment, and the size of the fuel source. Generators can be either portable or stationary, and can be powered by gasoline, diesel, natural gas, propane, or other fuel sources.
Generators are an essential part of power generation and are used to provide reliable, safe, and efficient power when traditional electricity sources are unavailable or unreliable.
2. What are the different types of generators available?
Generators are classified into different types based on the purpose they serve, the type of power they produce, and the type of fuel they use. Below are some of the most common types of generators:
- Portable Generators: These are lightweight and easy to transport. They are ideal for providing temporary power for outdoor activities such as camping, tailgating, or for use during natural disasters and power outages.
- Standby Generators: These are permanently installed units that are connected to the home or business’s electricity grid. They are designed to automatically start when power outages occur, providing a backup power source to essential services.
- Inverter Generators: These are portable generators that produce clean, stable power that is suitable for sensitive electronic devices, such as laptops and smartphones. They are quieter and more fuel-efficient than traditional portable generators.
- Diesel Generators: These are large stationary generators that use diesel fuel to generate power. They are commonly used for industrial and commercial applications, such as powering construction sites, factories, and hospitals.
- Natural Gas Generators: These are stationary generators that use natural gas to generate power. They are often used as backup power sources for businesses and other large operations.
- Solar Generators: These are portable generators that use solar energy to generate power. They are ideal for off-grid applications and can be used to charge batteries, power small appliances, and provide lighting.
3. How do I choose the right generator for my needs?
Choosing the right generator for your needs can be a difficult task. Here are some tips to help you make the right choice:
- Determine the wattage you need. Generators come in a range of wattages and it is important to choose one that is powerful enough to support all of your needs.
- Consider your fuel source. Different generators use different fuel sources, such as gasoline, diesel, or propane. Choose the fuel source that best meets your needs.
- Think about portability. If you plan to move your generator around, you’ll need one that is lightweight and easy to transport.
- Evaluate noise level. If you plan to use your generator in an area with noise restrictions, make sure to choose one that is quiet enough to comply with local laws.
- Compare prices. Generators can be expensive, so make sure you compare prices before making your purchase.
By following these tips, you should be able to find the perfect generator for your needs.
4. What safety precautions should I take when using a generator?
When using a generator, there are several important safety precautions that should be taken to ensure the safety of yourself and others around you. Below is a list of safety tips to observe when using a generator:
- Always read the user manual before operating the generator.
- Make sure to position the generator in a well-ventilated area.
- Keep the generator away from combustible material, such as gasoline, oil and other flammable liquids.
- Never overload the generator with more power than it can handle.
- Always keep the generator dry and away from any water sources.
- Ensure the power cords being used are in good condition and not damaged.
- Never try to repair the generator yourself unless you are a qualified technician.
- Always keep a fire extinguisher near the generator in case of emergency.
- Turn off the generator when not in use and disconnect all electrical appliances.
- Make sure the generator is grounded properly.
- Do not touch any of the generator’s exposed electrical parts while the engine is running.
5. What maintenance is required for a Generator to Keep it Running Efficiently?
A generator can be a great source of power, but it needs to be regularly serviced and maintained in order to keep it running efficiently. Here are some of the maintenance tasks that should be done to keep your generator in top condition:
- Oil Change: The oil in your generator should be changed at least once a year, more often if you use it frequently. Make sure to use the correct type of oil for your generator.
- Coolant Flush: The coolant in your generator should be flushed every two years. This helps to keep the engine cool and running at its peak performance.
- Spark Plug Replacement: The spark plug should be replaced every two to three years. This will help to ensure that your generator is operating at its optimal level.
- Air Filter Cleaning: The air filter should be cleaned or replaced every six months. This will help to keep the air intake clear and prevent the engine from becoming clogged.
- Fuel Filter Replacement: The fuel filter should be replaced every two years. This will help to make sure that the fuel is clean and free of debris, which can cause engine problems.
By performing these maintenance tasks regularly, you can ensure that your generator is running efficiently and reliably.
Conclusion
When it comes to generators, there is a lot to consider. In addition to researching different types of generators, reviews, and guides, it is important to understand the safety precautions and maintenance needs. Generators can provide reliable power in an emergency and can be used for camping, tailgating, and powering tools and appliances. With the right generator, you can have reliable power and peace of mind.
References
- Albright, R. (2018). The Ultimate Guide to Generators: How to Choose, Install and Maintain. McGraw Hill.
- Brown, B. (2020). Generator Reviews: A Comprehensive Guide. American Power Source.
- Kline, S. (2016). The Art of Generator Maintenance: Tips, Tricks, and Troubleshooting. Power Solutions.
- Lippman, M. (2019). Generator Guide: What to Look for When Buying a Generator. Power Pro.
- Roach, J. (2017). Generators for Beginners: What You Need to Know. Power Solutions.